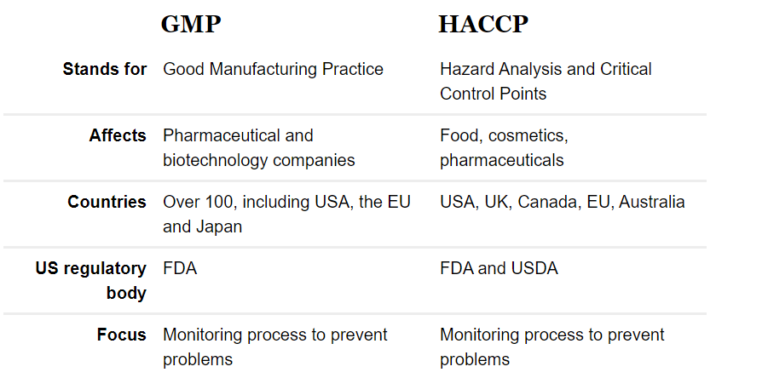
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices. GMPs are a set of guidelines that outline the minimum requirements for the production, processing, and handling of food products. GMPs are designed to help ensure the safety and quality of food products by establishing standard operating procedures and cleanliness requirements for food processing facilities.
GMPs are an important element of a food safety plan and are often used in conjunction with HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points). HACCP is a food safety management system that is used to identify and prevent potential hazards in the food production process, while GMPs focus on the overall cleanliness and operation of the facility.
Some examples of GMPs include:
- Proper handwashing and personal hygiene procedures
- Clean and sanitized equipment and utensils
- Adequate lighting and ventilation in the facility
- Pest control measures
- Proper storage and handling of raw materials and finished products
GMPs are typically enforced by regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). These agencies may conduct inspections of food processing facilities to ensure that they are following GMPs and other food safety regulations.